
The Real Estate Roundtable today requested federal bank regulators to reestablish immediately a troubled debt restructuring (TDR) program for commercial real estate that would give financial institutions increased flexibility to refinance loans with borrowers and lenders. (Roundtable letter to regulators, March 17)
Roundtable Liquidity Concerns
Fed Intervention 
Remote Work

The Roundtable’s letter concludes by urging the federal regulators to “take action immediately to provide increased latitude for financing institutions to work constructively with borrowers. Such action will avert what we believe would be an unnecessary crisis.”
# # #
 A coalition of trade organizations that includes The Real Estate Roundtable asked the IRS yesterday to issue regulatory guidance clarifying that unrealized gains and losses are not subject to tax under the new corporate alternative minimum tax (CAMT). Enacted under the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, CAMT levies a 15% minimum tax on the adjusted financial statement income (book income) of certain large corporate taxpayers. (Coalition letter, March 15)
A coalition of trade organizations that includes The Real Estate Roundtable asked the IRS yesterday to issue regulatory guidance clarifying that unrealized gains and losses are not subject to tax under the new corporate alternative minimum tax (CAMT). Enacted under the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, CAMT levies a 15% minimum tax on the adjusted financial statement income (book income) of certain large corporate taxpayers. (Coalition letter, March 15)
CAMT Implementation
Coalition Weighs In 
The Roundtable’s Tax Policy Advisory Committee (TPAC) and its partner organizations will continue to work with federal regulators on the CAMT guidance to prevent the unintended taxation of unrealized real estate gains and losses.
# # #

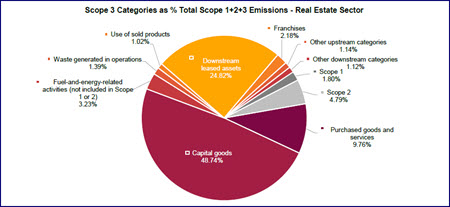
Reports released this month show the challenges companies face to quantify indirect “Scope 3” GHG emissions that emanate from an organization’s value chain. These studies support recent remarks from U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Chair Gary Gensler that Scope 3 reporting is not “well-developed,” and “adjustments” could be made to the agency’s highly anticipated climate risk reporting rule. (CNBC, March 6 and Roundtable Weekly, March 10)
Reporting Categories
Real Estate & Scope 3
Executives on Scope 3

Separately, Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer (D-NY) this week commented on a proposed House of Representatives energy package (H.R. 1), which focused on measures impacting fossil fuels, as a "non-starter" for congressional negotiations. (Politico, March 15)
# # #