The federal government reopened late Wednesday after a 43-day shutdown, the longest in U.S. history, as Congress approved a short-term funding bill keeping agencies running through Jan. 30, 2026. (The Hill, Nov. 13)
State of Play
- The Senate approved the bipartisan package Monday night in a 60–40 vote, with seven Democrats and Angus King (I-ME) joining Republicans to advance the deal. Sen. Rand Paul (R-KY) was the only Republican “no” vote. (Punchbowl News, Nov. 12)
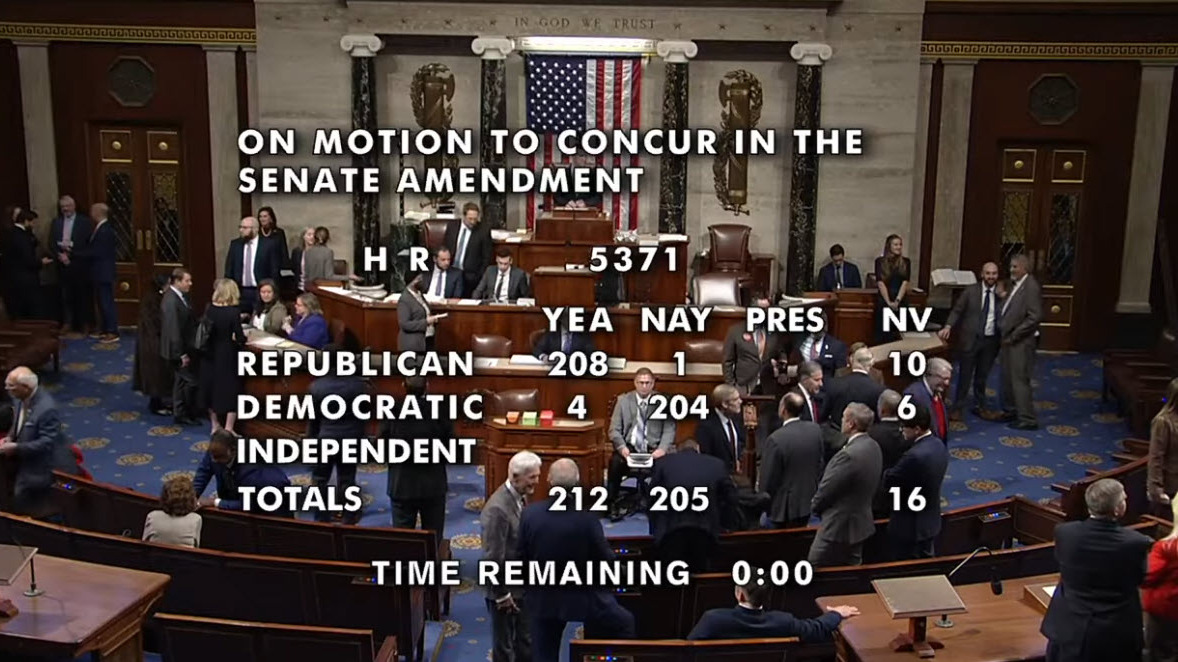
- The House passed the measure on a 222–209 vote, with six Democrats joining all but two Republicans, on Wednesday night. President Trump signed the bill hours later, ending weeks of halted federal services, frozen benefits, and widespread economic disruptions. (Washington Post, Nov. 12)
- “This is no way to run a country,” Trump said while signing the bill that ended the shutdown. “I hope we can all agree the government should never be shut down again.” (Roll Call, Nov. 12)
- The agreement includes full-year FY2026 appropriations for Agriculture, Veterans Affairs, and the Legislative Branch, while extending funding for all other agencies for 11 additional weeks. The deal reverses thousands of federal layoffs proposed during the shutdown and guarantees back pay for more than 1.25 million furloughed or unpaid federal employees. (Punchbowl News, Nov. 13)
- In exchange, Senate Majority Leader John Thune (R-SD) guaranteed Senate Democrats a mid-December vote on extending the Affordable Care Act’s enhanced tax credits. Extending the health insurance subsidies was the Democrats’ primary demand during the shutdown. Speaker Mike Johnson (R-LA) made no promise for a similar vote in the House. (Politico, Nov. 12)
What’s Restored: NFIP, HUD Programs, Federal Services

- National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP): The NFIP, which lapsed during the shutdown, has been temporarily reauthorized through Jan. 30. New policies can now be issued and existing policies renewed, removing a major barrier for commercial and residential transactions. This is the program’s 34th short-term extension since 2017 as lawmakers continue pursuing a long-term fix.
- Section 8 & HUD Rental Assistance: HUD is authorized to repurpose carryover funds within the Housing Choice Voucher Program to ensure the full renewal of existing rental assistance at current fair market rents through Jan. 30. This measure prevents disruptions for property owners and the millions of low-income households relying on stable voucher support. (PoliticoPro, Nov. 11)
- Other Federal Operations: SNAP benefits for 42 million Americans will resume in full, while air traffic control, TSA operations, farm loan processing, and other federal services return to normal as national parks and benefits offices reopen. The agreement also halts proposed federal layoffs through the end of January.
What’s Next
- Congress now has 77 days to complete the remaining FY2026 appropriations bills. (House Appropriations Committee Press Release, Nov. 12)
- “Reopening the government is a welcome and necessary step that restores stability to federal operations, housing programs, and the broader economy,” said Jeffrey DeBoer, President and CEO of The Real Estate Roundtable. “It also restores the federal economic data that lenders and investors rely on to plan and facilitate transactions.”
- Major hurdles remain, including the lack of an agreed-upon topline spending level, the Senate’s push to advance a five-bill package that includes Transportation-HUD, and the House’s need to accelerate committee work after weeks of inactivity.
- FY2026 funding bills for Energy, EPA, Homeland Security, State, and Treasury/IRS still require difficult bipartisan negotiations.
Another shutdown is possible if Congress fails to meet the Jan. 30 deadline.