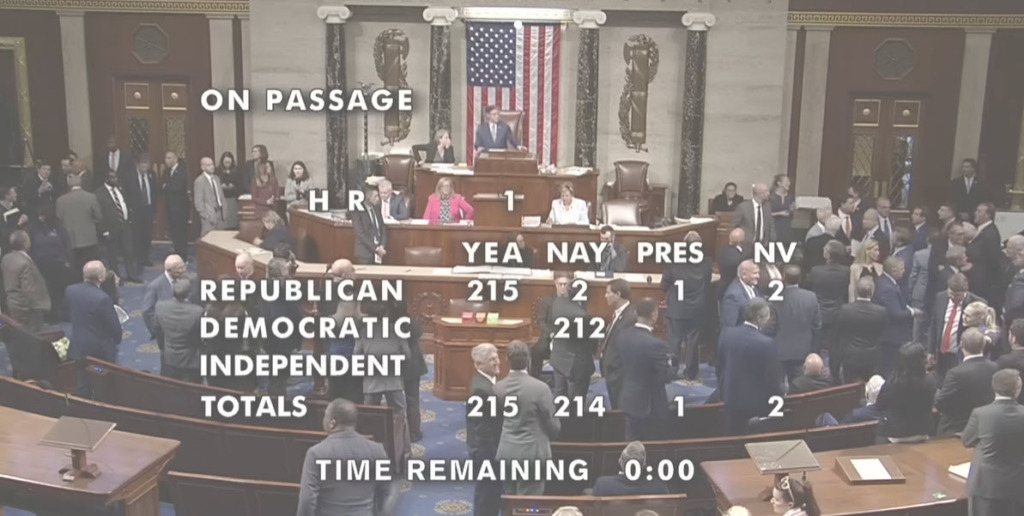
President Donald Trump signed the One Big Beautiful Bill Act (OBBB Act) into law on July 4, the culmination of months of work by congressional Republicans to reshape federal tax and spending policies. The legislation included provisions long advocated by The Real Estate Roundtable (RER), such as a significant expansion of affordable housing tax incentives, accelerated depreciation for property improvements, and reform of tax accounting rules for condominium construction.
RER Summary of Real Estate Related Provisions
Affordable Housing Boost
- The OBBB Act enacts landmark changes to address the nation’s housing shortage through enhancements to long-standing development incentives. (Roundtable Weekly, July 3)
- The OBBB Act expands the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC) by permanently increasing state LIHTC allocations by 12% and reducing the private activity bond financing requirement for 4% LIHTC projects from 50% to 25%. The latter provision will allow more affordable housing projects to receive tax credits without a direct allocation from the state.
- The bill’s overhaul of tax provisions is projected to support the development of up to 1.2 million affordable rental units over the next decade. (PoliticoPro, July 9)
- These changes to the LIHTC represent “the single largest increase in affordable housing development resources in at least 25 years,” said Peter Lawrence, chief public policy officer at Novogradac. (PoliticoPro, July 9)
Other OBBB Tax Changes Will Stimulate Housing Construction, Property Upgrades, and Real Estate Investment

- Bonus Depreciation: The new tax law permanently restores immediate 100% expensing of qualifying capital expenditures, including appliances, fixtures, leasehold improvements, and interior improvements to nonresidential property. The provision will encourage capital investment and spur real estate improvements by reducing the after-tax cost of modernizing and upgrading existing properties. (RER Summary of Real Estate Related Provisions)
- Condominium Construction: OBBB ends a discriminatory tax accounting rule that unfairly created phantom income for condo developers with respect to the pre-sale of units. The prior rule requiring condo developers to use the percentage of completion method of accounting raised hurdles for construction financing and discouraged new housing construction. OBBB will allow developers to use the completed contract method, aligning tax liability with actual receipts.
- Opportunity Zones (OZs): OBBB permanently extends the Opportunity Zones (OZ) tax incentives, establishes a new designation of OZ census tracts every 10 years, and going forward, creates a 5-year rolling deferral period for capital gains invested in opportunity funds. Since their enactment in 2017, OZs have attracted over $120B in capital for low-income communities, with most investment going towards new housing and other productive real estate development. (Joint Committee on Taxation, 2024; Novogradac, Feb. 2025; Economic Innovation Group, March 2025)
- On the latest episode of the Walker Webcast’s Most Insightful Hour in CRE, RER member Willy Walker (Chairman and CEO, Walker & Dunlop) and economist Dr. Peter Linneman (Principal, Linneman Associates) discussed the OBBB Act, tariffs, impacts on construction costs, affordable housing, single and multifamily supply, CRE markets, and much more. (Watch Webcast) (ConnectCRE, July 9)
State-Level Initiatives Strengthen Federal Housing Efforts
- Rising construction costs and ongoing affordability challenges have prompted states to complement federal initiatives like LIHTC.
- States such as Tennessee, Georgia, and Michigan have introduced innovative financing programs—including state-level tax credits and tax increment financing (TIF), leveraging future tax revenues generated by increased property values to sustainably fund and accelerate housing projects. (GlobeSt. July 11)
- This week, RER member David O’Reilly (CEO, Howard Hughes Holdings) appeared on CNBC to discuss interest rates, housing market, and consumer demand.
- Florida will eliminate its longstanding tax on commercial rents effective Oct. 1, 2025, becoming the first and only state to repeal the tax. The move is expected to reduce costs for tenants across office, industrial, and retail sectors, enabling businesses to reinvest capital into operations, local communities, and real estate. (GlobeSt. July 10)
Looking Ahead

- Senate Finance Committee Chair Mike Crapo (R-ID) said this week that Republicans are eyeing a second party-line reconciliation package this fall to pursue policy priorities left out of the final OBBB Act.
- “I’ve always been in favor of a three-bill strategy and there’s a ton of things that we need to do,” Sen. Crapo said (Politico, July 9).
- GOP leaders have discussed reworking provisions flagged by the Senate parliamentarian during OBBB Act negotiations, potentially reviving items such as additional tax reforms and deeper spending cuts.
- House Speaker Mike Johnson (R-LA) and House Budget Chair Jodey Arrington (R-TX) are also pushing for fall action, though Sen. Crapo cautioned that timelines remain fluid. (Politico, July 8 | Fox News, July 6)
- “We’ve been planning a second reconciliation bill for the fall attached to the next fiscal year, and then potentially one in the spring,” Speaker Johnson said on Fox News Sunday. “That’s my plan. Three reconciliation bills before this Congress is over. I think we can do that.” (Fox News, July 6)
“Revenge Tax” Provision
- The final OBBB Act excluded a provision opposed by The Roundtable that would have raised taxes on foreign investment that originated in countries deemed to have unfair tax policies. Proposed Section 899 could reappear, however, if international tax talks to exempt US companies from a global tax deal falter. (Roundtable Weekly, June 27)
The G7 agreement to agreement is still only a “statement of intent,” with implementation details unresolved, raising the risk that Section 899 could return in a future reconciliation package, according to Tax Notes. “Republicans made clear they’d bring it back if G7 partners slow-walk the deal,” said Danielle Rolfes of KPMG. (Tax Notes, July 10)