Policymakers marked up a series of housing and energy measures this week focused on streamlining project approvals, updating efficiency standards, and addressing federal funding for state and local energy laws. The discussions highlighted bipartisan momentum around reforms to bolster grid reliability and reduce housing costs.
SPEED Act Mark Up
- The House Natural Resources Committee on Thursday marked up the Standardizing Permitting and Expediting Economic Development (SPEED) Act (H.R. 4776) and adopted a bipartisan amendment limiting executive-branch authority to cancel energy project permits, a key issue in broader negotiations. (PoliticoPro, Nov. 20 | Watch Mark-Up)
- The bill would amend the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) to streamline environmental reviews and reduce litigation delays for projects requiring federal funding and permits. (The Hill, Nov. 17)
- House Natural Resources Committee Chair Bruce Westerman (R-AR) said, “NEPA reform helps everything. “It helps electrical transmission. It helps pipelines. It helps traditional energy sources. It helps new energy sources. It helps transportation and infrastructure projects.” If NEPA reform passes “everybody wins,” he added.
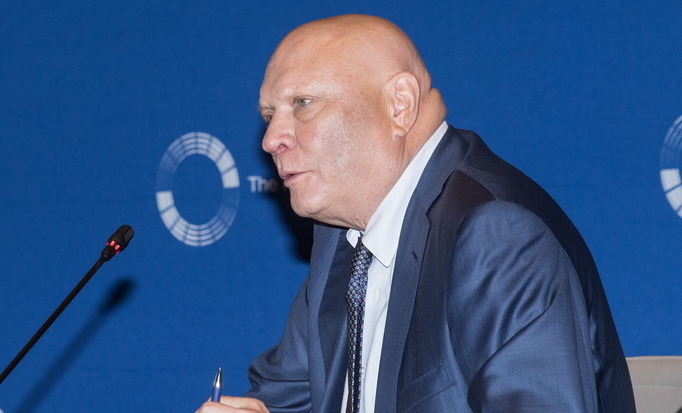

- Jeffrey DeBoer, RER President and CEO, said, “Permitting reform is essential to strengthening the nation’s electric grid and infrastructure. The current patchwork of federal, state and local approvals delays the delivery of affordable, reliable power to homes and commercial buildings. The Roundtable supports efforts—like the SPEED Act—to modernize permitting, improve grid resilience, and ensure the infrastructure needed for long-term economic growth.”
- The SPEED Act is expected to continue to draw bipartisan support in the House. Ongoing Senate negotiations are reportedly addressing renewable-energy protections, emissions-reduction provisions, and a potential broader package blending transmission policy, clean-energy safeguards, and litigation limits. (E&E News, Nov. 17)
- Rep. Scott Peters (D-CA) called the bill a “huge step forward,” and urged Democratic colleagues to support it, while seeking further adjustments to curb the executive branch’s ability to cancel energy project permits. (Press Release | PoliticoPro, Nov. 20)
House Energy & Commerce Mark Ups
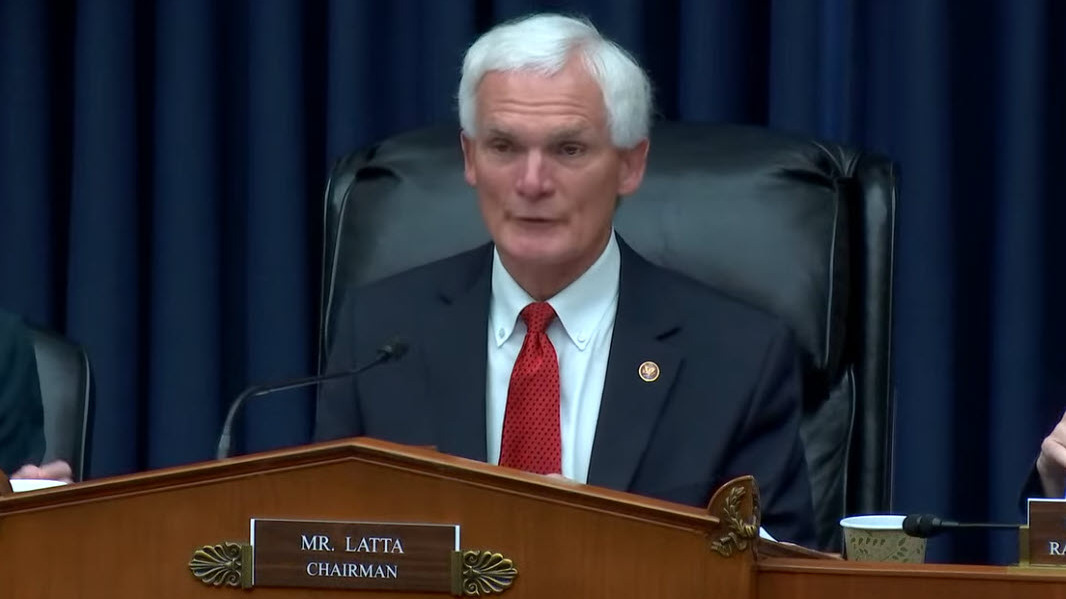

- On Wednesday, a House Energy and Commerce subcommittee marked up eight energy-related bills, reflecting contrasting approaches to energy affordability and building efficiency standards as lawmakers debate rising energy and housing costs. (PoliticoPro, Nov. 19 | Committee Press Release )
- The subcommittee approved several CRE-relevant bills that now move to the full committee for consideration.
- Energy Choice Act (H.R. 3699): Advanced by voice vote. Aims to prevent state/local laws that would ban the use of natural gas in buildings. (A “ban on gas bans” aligns with RER’s 20-Point Policy Guide on Building Performance Standards)
- Affordable Housing Over Mandating Efficiency Standards Act (H.R. 5184): Advanced by voice vote. Aims to reduce stringent energy efficiency codes for manufactured housing and negatively impact housing affordability.
- Homeowner Energy Freedom Act (H.R. 4758): Approved 16–14 along party lines. Aims to eliminate federal funding under the Biden-era Inflation Reduction Act, which provides grants to states and localities to support the highest-level energy codes, building electrification mandates, and other building performance standards. (Roundtable Weekly, Feb. 28)
- Energy Subcommittee Chair Bob Latta (R-OH) said, “The legislation before us today represents an opportunity for this committee to implement reforms that re-prioritize energy efficiency policies toward the items that matter most to consumers: Affordability, availability, and durability.” (PoliticoPro, Nov. 19)
Climate Disclosure Law
- In other energy news this week, a federal appeals court issued a preliminary injunction halting enforcement of California’s SB 261, requiring companies with at least $500M in global revenue to report climate-related financial risks starting January 2026. (ESG Dive | PoliticoPro, Nov. 18)
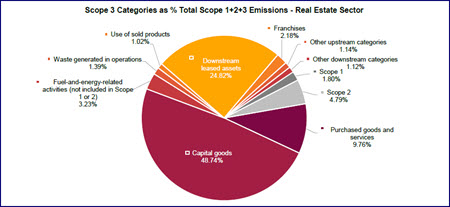
- The court blocked SB 261, pending litigation over First Amendment concerns. It did not block SB 253, which requires corporations with $1B+ in revenue to begin reporting scope 1 and 2 emissions in 2026, and scope 3 in 2027. The trial on the First Amendment claim is scheduled for October 2026. (RER Fact Sheet, 2023; RW Sept. 2023)
RER will continue working with policymakers as Congress weighs permitting reform and energy policy measures that directly affect commercial real estate investment, housing supply, and the reliability of the nation’s power grid